In the house, we all have different tastes in movies and shows. So, do you buy a separate Netflix account for everyone? Of course not. Instead, you set up different profiles, and each person gets their own watchlist, recommendations, and history. That way, everyone has full freedom, privacy, and it doesn’t cost extra.
That’s exactly what organizations do with server virtualization. Instead of setting up separate dedicated servers for each task or user, they create virtual servers. Each virtual server acts independently, showing only what’s needed and keeping other activities separate and secure.
Sounds interesting? Keep reading. We’ll break down how server virtualization works. Also cover the benefits it brings and the challenges it comes with.
How Server Virtualization Works
A single server runs a bunch of virtual servers at once. Each one acts like its own computer. But all of them are still sharing the same hardware. Companies love this because it means they can use their servers properly, instead of letting storage free.
To make this work, you need a hypervisor. It decides who gets what: CPU, memory, storage. And it keeps the VMs from interfering with each other. There are two main kinds:
- Type 1 (Bare-metal): Runs directly on the server. Fast. Efficient.
- Type 2 (Hosted): Runs on top of another operating system. More flexible, a tiny slower.
The hypervisor also keeps an eye on everything. If one VM isn’t using much, it can give the extra resources to another one that needs it.
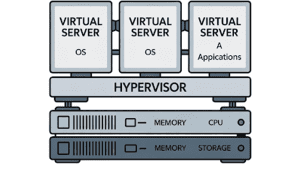
So basically, one server becomes a bunch of independent little servers. Each one works on its own. Resources are used better. IT teams can manage stuff without sweating over every problem. And everything stays safe and separate.
Types of Server Virtualization
There are three different types of server visualization, each has its own approach to running virtual machines (VMs) on a physical server.
Full Virtualization: Full virtualization separates each VM completely from the host server and from other VMs. That way, each VM runs its own operating system and applications independently.
Pros:
- Complete isolation; issues in one VM don’t affect others.
- Supports multiple operating systems on the same server.
- Ideal for testing different software setups.
Cons:
- Hypervisor consumes some resources, slightly reducing performance.
- More resource-intensive than other virtualization types.
Para-Virtualization: In para-virtualization, VMs are aware of the hypervisor and sometimes of each other. They share some responsibilities for managing resources, reducing overhead.
Pros:
- Lower overhead than full virtualization.
- Efficient use of server resources.
Cons:
- Requires host OS support and compatible setup.
- Less flexible than full virtualization for different OSes.
OS-Level (Hosted) Virtualization: OS-level virtualization relies on the host operating system to manage all VMs. Each VM runs as an isolated container, sharing the host OS kernel.
Pros:
- Highly efficient; supports many VMs on one server.
- Easier to manage and maintain.
Cons:
- All VMs must use the same OS as the host.
- If the host OS fails, all VMs go down.
- Isolation is weaker compared to full virtualization.
Benefits of Server Virtualization
- Equipped server resources smartly, instead of spending on physical hardware.
- Save cost and allocate the extra server capacity where required.
- With one hardware, you can create virtual servers of different OSes and applications.
- Locked the server with different tasks, can improve performance of the applications
- Add and replace virtual servers to manage workload.
- Backs up the database, that secure the information in any data corrupt issues.
- Reduce the cyber attack effect, because if any virtual server gets affected, it will not transfer to the others.
Challenges of Server Virtualization
Despite the many benefits of server virtualization, there are still some challenges:
- Software licensing can be complex (and costly) because one physical server might host dozens of different VMs with a wide range of applications and services. For instance, full server virtualization means each VM has its own OS, and each OS requires a separate license.
- A host server failure can affect all of its VMs. So 10 applications go down instead of just one.
- VM sprawl can become an issue if IT doesn’t stay on top of where VMs are and how they’re being used. It’s so easy to spin up new instances that many VMs are used temporarily for testing and then abandoned. If they’re not actually deleted, they could remain in the background and continue to consume power and resources that active VMs need.
- If VMs aren’t planned and created carefully, server performance can slow down when too many resource-heavy VMs are running on the host, especially with networking and memory.
How to Implement Server Virtualization
- Create a plan: Make sure everyone knows why you even need virtualization before starting. Check costs, think about complexity, and see how it fits in your business plan.
- See what’s out there: Check hardware, software options, and even what competitors are using. Knowing this early saves a lot of headaches later.
- Test and experiment: Spin up a few VMs on a small scale and see how it works day to day. IT will be running it, so they need to know what could go wrong and feel confident.
- Consider business needs: Make sure the solution covers security, compliance, disaster recovery, and fits your IT setup overall.
- Start small, then scale: Don’t go all-in at once. Try non-critical systems first, learn the ropes, then expand.
- Set guidelines: Decide how VMs are created, monitored, and retired. This helps control resources, avoid sprawl, and keep things organized.
- Pick the right tools: Extra software and features can make managing VMs much easier.
- Don’t forget automation: It makes everything smoother, saves manual work, and IT should know how to use it.
If it feels messy for you, just leave it to us! We’ve been doing this for a long time and know how to smartly create server chains and logic so that resources are always allocated exactly where they’re needed.
Tell Us What You Need – Start Your Journey Today!
Share your project requirements, and we’ll guide you through a seamless development journey to bring your ideas to life.
FAQs
What is server virtualization?
Server virtualization is the process of running multiple virtual servers on a single physical server. Each virtual server works independently, using shared resources efficiently, which saves hardware costs and improves flexibility.
How does server virtualization improve performance?
It improves performance by distributing resources like CPU, memory, and storage dynamically across virtual servers. Tasks run smoother because each VM gets what it needs without waiting for other processes to finish.
Is server virtualization secure?
Server virtualization keeps each virtual server isolated, so if one server is compromised, others remain unaffected. Proper setup and monitoring further strengthen security across all operations.
Can all applications run on virtual servers?
Most applications work well on virtual servers, but some resource-heavy or specialized software might need dedicated hardware. Testing in a virtual environment first helps ensure smooth performance.
How much does server virtualization cost?
Costs vary depending on hardware, software, and licensing needs. It often reduces overall IT expenses since fewer physical servers are required while giving flexibility to add or remove virtual servers as needed.
How do I manage multiple virtual servers efficiently?
Management becomes simple with the right tools and automation. Regular monitoring, resource allocation, and following best practices prevent VM sprawl and ensure smooth daily operations.
What happens if a host server fails?
A host server failure can affect all hosted VMs, so proper backup and disaster recovery planning is crucial. Redundant setups and failover strategies minimize downtime and keep services running.
How can Pure Website Design help with server virtualization?
Pure Website Design can set up virtual servers tailored to each part of your operations. That ensures resources are smartly allocated, performance stays high, and IT management remains stress-free.
Why choose Pure Website Design for virtualization setup?
The team at Pure Website Design brings experience in creating efficient server chains and logic. Every virtual server is configured for security, easy management, and maximum resource use, letting operations run smoothly without extra hassle.
Conclusion
Server virtualization can boost computer performance and improve security as well. The trick is using it the right way, done correctly, it doesn’t just make operations smoother, it also saves budget and resources.
To get things running perfectly, contact us. Pure Website Design has expert developers who set up virtual servers for each part of your operations team, giving everyone private space and a clear, easy-to-manage work environment.